HDMA examples: Difference between revisions
(Add list of dynamic HDMA table techniques, added HDMA textbox wipe example) |
(→Dynamic HDMA tables: Add pseudocode for a double-buffered horizontal offset parallax effect) |
||
| Line 363: | Line 363: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
=== Double buffered HDMA tables === | |||
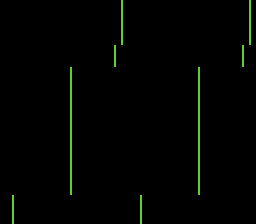
[[File:Hdma_double_buffered_parallax.png|thumb|Simple horizontal offset parallax effect]] | |||
<pre> | |||
Variables: | |||
hdmaBufferA u8[512] - first HDMA buffer | |||
hdmaBufferB u8[512] - second HDMA buffer | |||
activeHdmaBuffer u8 - Flag to determine which buffer to write to | |||
cameraX u16 - Camera's X position | |||
// TIMING: Force-Blank, HDMA disabled | |||
// Uses HDMA channel 7 | |||
subroutine Setup: | |||
assert .bankbyte(hdmaBufferA) == .bankbyte(hdmaBufferB) | |||
DMAP7 = 2 // one write-twice register, to PPU | |||
BBAD7 = .lobyte(BG1HOFS) // B-bus address | |||
B1B7 = .bankbyte(hdmaBufferA) // HDMA Table A-bus bank | |||
// HDMA Table address is written during VBlank | |||
// The hdmaBuffer must be populated before the next VBlank routine | |||
BuildHdmaTable() | |||
// TIMING: Screen active, in VBlank | |||
// TIMING: MUST NOT be executed in a lag frame | |||
// Uses HDMA channel 7 | |||
subroutine VBlank: | |||
// Set HDMA table word address (depending on which buffer was last used by the MainLoop) | |||
if activeHdmaBuffer == 0: | |||
A1T7 = .loword(hdmaBufferB) | |||
else: | |||
A1T7 = .loword(hdmaBufferA) | |||
// Enable HDMA channel 7 | |||
HDMAEN = 1 << 7 | |||
// TIMING: MUST NOT be called more than once per frame | |||
function GetNextHdmaBuffer() -> *u8 | |||
if activeHdmaBuffer == 0: | |||
activeHdmaBuffer = 1 | |||
return &hdmaBufferA | |||
else: | |||
activeHdmaBuffer = 0 | |||
return &hdmaBufferB | |||
// TIMING: MUST NOT be called more than once per frame | |||
subroutine BuildHdmaTable: | |||
buffer = GetNextHdmaBuffer() | |||
// Four non-repeat HDMA entries | |||
// Remember, all `u8` writes MUST be <= 128 | |||
buffer[ 0] as u8 = 45 | |||
buffer[ 1] as u16 = cameraX >> 3 | |||
buffer[ 3] as u8 = 22 | |||
buffer[ 4] as u16 = cameraX >> 2 | |||
buffer[ 6] as u8 = 128 | |||
buffer[ 7] as u16 = cameraX | |||
buffer[ 9] as u8 = 128 | |||
buffer[10] as u16 = cameraX << 1 | |||
// End HDMA table | |||
buffer[12] as u8 = 0 | |||
</pre> | |||
== Links == | == Links == | ||
Revision as of 02:50, 4 December 2022
Examples for using HDMA.
Transfer patterns
The following is a suggested list of PPU registers that can be used in the various HDMA transfer patterns.
One register (DMAP pattern 0)
This pattern reads/writes a single byte to a single address on the B-bus (+0).
This pattern should not be used on write-twice or read-twice registers.
- BG Mode:
BGMODE - Mosaic Settings:
MOSAIC - BG Settings:
BG1SC,BG2SC,BG3SC,BG4SC,BG12NBA,BG34NBA - Mode 7 settings:
M7SEL - CGRAM address:
CGADD- A future HDMA channel should write to
CGDATAon the same scanline as theCGADDwrite.
- A future HDMA channel should write to
- Window settings:
W12SEL,W34SEL,WOBJSEL,WBGLOG,WOBJLOG - Layer enable:
TM,TS,TMW,TSW - Color math:
CGWSEL,CGADSUB - Screen Mode/Video Select:
SETINI - Fixed color data:
COLDATA- Only a single B/G/R channel can be changed in this pattern (unless multiple channels contain the same value). See
COLDATAfor more details.
- Only a single B/G/R channel can be changed in this pattern (unless multiple channels contain the same value). See
Two registers (DMAP pattern 1)
This pattern reads/writes two bytes to two addresses on the B-bus (+0, +1). It is useful when writing to two adjacent byte registers.
This pattern must not be used on write-twice or read-twice registers.
- Window 1 left and right position:
WH0&WH1 - Window 2 left and right position:
WH2&WH3 - Window mask settings:
W12SEL&W34SEL,W34SEL&WOBJSEL - Window mask logic:
WBGLOG&WOBJLOG - Layer Enable:
TM&TS,TMW&TSW - Color math settings:
CGWSEL&CGADSUB
One register, write twice (DMAP pattern 2)
This pattern reads/writes two bytes to a single write-twice or read-twice register on the B-bus (+0, +0).
- BG horizontal scroll offset:
BGnHOFS - BG vertical scroll offset:
BGnVOFS - Mode 7 matrix:
M7A,M7B,M7C,M7D,M7X,M7Y - CGRAM data:
CGDATA- Note: A previous HDMA channel should set the CGRAM address on the same scanline as a
CGDATAwrite
- Note: A previous HDMA channel should set the CGRAM address on the same scanline as a
- Fixed color data:
COLDATA- Only two of the three B/G/R channels can be changed in this pattern (unless two channels share the same value). See
COLDATAfor more details.
- Only two of the three B/G/R channels can be changed in this pattern (unless two channels share the same value). See
Two registers, write twice (DMAP pattern 3)
This pattern reads/writes four bytes to two adjacent write-twice or read-twice registers on the B-bus (+0, +0, +1, +1).
- BG scroll offsets:
BGnHOFS&BGnVOFS - 2 adjacent mode 7 matrix values:
M7A&M7B,M7C&M7D,M7X&M7Y - CGRAM address and data:
CGADD&CGDATA- This transfer will write two values to the CGRAM address, followed by a color word value to
CGDATA. - The first byte will be ignored by the PPU, the second byte contains the target CGRAM address (palette index), the third and forth bytes contain the color data.
- This transfer will write two values to the CGRAM address, followed by a color word value to
Four registers (DMAP pattern 4)
This pattern reads/writes four bytes to four addresses on the B-bus (+0, +1, +2, +3).
This pattern must not be used on write-twice or read-twice registers.
- All four window positions:
WH0&WH1&WH2&WH3
HDMA Tables
HDMA tables are made up of multiple HDMA entries. Each entry starts with a Line-Counter byte, followed by register data. The type of HDMA entry depends on the Line-Counter byte:
- Line-Counter 0: End of HDMA table. The HDMA channel will be deactivated and will remain deactivated until the start of the next frame (even if HDMAEN is written to mid-frame).
- Line-Counter 0x01-0x80: non-repeating HDMA entry. Writes once then waits LineCounter scanlines.
- Line-Counter 0x81-0xFF: repeating HDMA entry. Writes every scanline for the next LineCounter - 0x80 scanlines.
Non-repeat HDMA entries
A non-repeat HDMA entry (0x01 <= Line-Counter <= 0x80) is hdma_transfer_bytes + 1 bytes in size. It consists of the Line-Counter byte, followed by the data to transfer on the next Horizontal Blanking Period. Afterwards, the HDMA controller will wait for Line-Counter scanlines before processing the next HDMA entry.
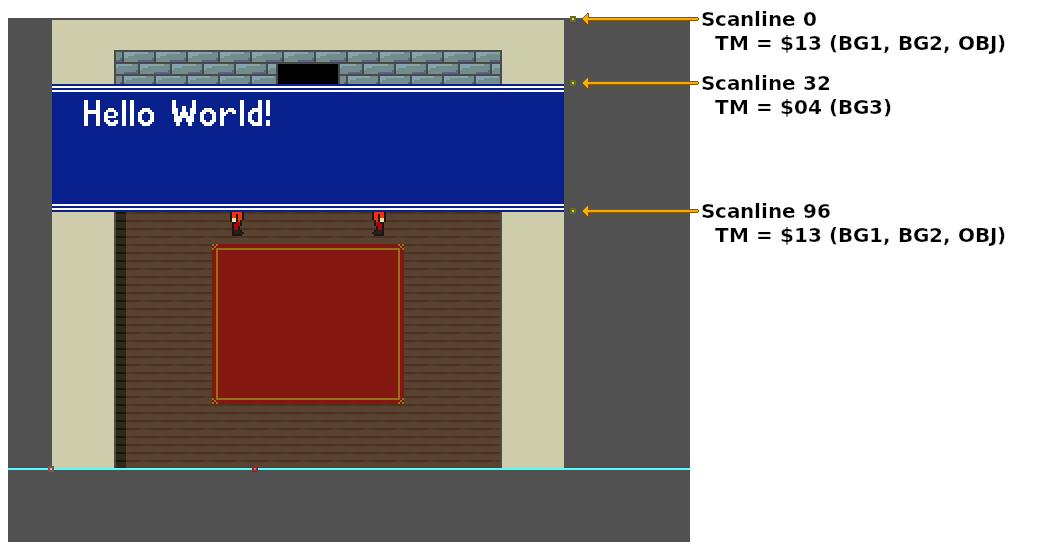
DMAP7 = 0 // one register, to PPU
BBAD7 = .lobyte(TM) // B-bus address
A1T7 = .loword(HdmaTable) // HDMA Table A-bus address
B1B7 = .bankbyte(HdmaTable)
// Enable HDMA channel 7
// (HDMAEN should be written to during VBlank)
HDMAEN = 1 << 7
// HDMA Table targeting the `TM` register (One register transfer pattern).
HdmaTable:
db 32 // 32 scanlines, non-repeat entry
db 0x13 // TM = BG1, BG2, OBJ
db 64 // 64 scanlines, non-repeat entry
db 0x04 // TM = BG3
db 1 // 1 scanline, non-repeat entry
db 0x13 // TM = BG1, BG2, OBJ
db 0 // End HDMA table
Each non-repeat HDMA entry is a maximum of 128 scanlines tall. Any HDMA entry with more then 128 scanlines must be split in two, with each entry containing the same data values.
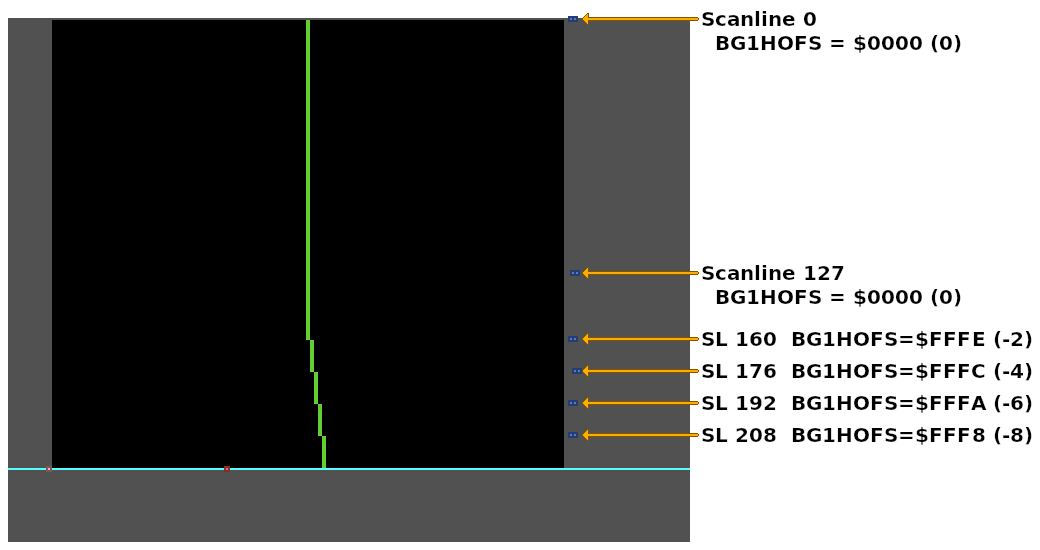
DMAP7 = 2 // one write-twice register, to PPU
BBAD7 = .lobyte(BG1HOFS) // B-bus address
A1T7 = .loword(HdmaTable) // HDMA Table A-bus address
B1B7 = .bankbyte(HdmaTable)
// Enable HDMA channel 7
// (HDMAEN should be written to during VBlank)
HDMAEN = 1 << 7
// HDMA Table for the `BG1HOFS` register (one register, write twice transfer pattern).
HdmaTable:
// 160 scanlines with BG1HOFS = 0
// Too many scanlines to fit in a single HDMA entry.
db 127 // 127 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw 0
db 33 // 33 scanlines, non-repeat entry (+127 = 160 scanlines total)
dw 0 // Same data value as the previous entry
// Change BG1HOFS every 16 scanlines
db 16 // 16 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw -2
db 16 // 16 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw -4
db 16 // 16 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw -6
db 16 // 16 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw -8
db 0 // End HDMA table
Repeating HDMA entries
A repeating HDMA entry (Line-Counter >= 0x81) is hdma_transfer_bytes * (line_counter - 0x80) + 1 bytes in size. It consists of the Line-Counter byte, followed by count (line_counter - 0x80) values to transfer. For the next count scanlines, the HDMA controller will transfer hdma_transfer_bytes bytes of data during the next count Horizontal Blanking Periods.
Each repeating HDMA entry is a maximum of 127 scanlines tall. Any repeating HDMA entry with more than 127 scanlines must be split in two.
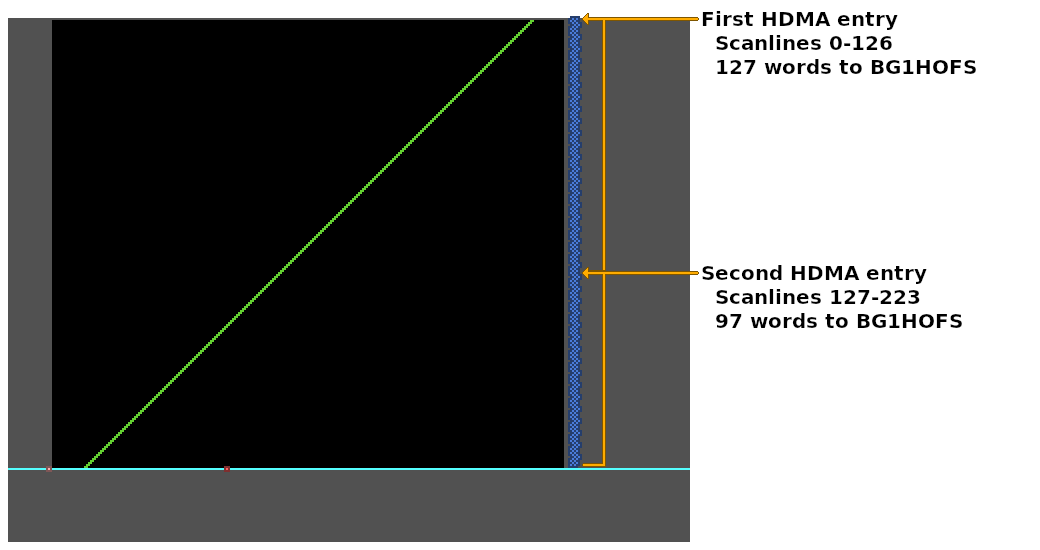
DMAP7 = 2 // one write-twice register, to PPU
BBAD7 = .lobyte(BG1HOFS) // B-bus address
A1T7 = .loword(HdmaTable) // HDMA Table A-bus address
B1B7 = .bankbyte(HdmaTable)
// Enable HDMA channel 7
// (HDMAEN should be written to during VBlank)
HDMAEN = 1 << 7
// HDMA Table for the `BG1HOFS` register (one register, write twice transfer pattern).
HdmaTable:
db 0x80 | 127 // 127 scanlines, repeat entry (maximum number of repeat scanlines per entry)
// 127 words (254 bytes) of BG1HOFS data for the next 127 scanlines
dw 144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159, 160, 161, 162, 163, 164, 165, 166, 167, 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, 173, 174, 175, 176, 177, 178, 179, 180, 181, 182, 183, 184, 185, 186, 187, 188, 189, 190, 191, 192, 193, 194, 195, 196, 197, 198, 199, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 208, 209, 210, 211, 212, 213, 214, 215, 216, 217, 218, 219, 220, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225, 226, 227, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 234, 235, 236, 237, 238, 239, 240, 241, 242, 243, 244, 245, 246, 247, 248, 249, 250, 251, 252, 253, 254, 255, 256, 257, 258, 259, 260, 261, 262, 263, 264, 265, 266, 267, 268, 269, 270
db 0x80 | 97 // 97 scanlines, repeat entry (+127 = 224 scanlines total)
// 97 words (194 bytes) of BG1HOFS data for the next 97 scanlines
dw 271, 272, 273, 274, 275, 276, 277, 278, 279, 280, 281, 282, 283, 284, 285, 286, 287, 288, 289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 296, 297, 298, 299, 300, 301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 306, 307, 308, 309, 310, 311, 312, 313, 314, 315, 316, 317, 318, 319, 320, 321, 322, 323, 324, 325, 326, 327, 328, 329, 330, 331, 332, 333, 334, 335, 336, 337, 338, 339, 340, 341, 342, 343, 344, 345, 346, 347, 348, 349, 350, 351, 352, 353, 354, 355, 356, 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 362, 363, 364, 365, 366, 367
db 0 // End HDMA table
Indirect HDMA
All HDMA entries in HDMA indirect mode (bit 6 of DMAPn set) are 3 bytes in size. They consist of the Line-Counter byte followed by a word address. This word address is combined with the DASBn (Indirect HDMA Bank) register and points to the data to transfer to/from the B-bus.
The format and behaviour of the Line-Counter byte is the same as the HDMA direct addressing mode.
Indirect mode can be used to map an unbroken contiguous array of 224 register values to two HDMA repeat entries.
DMAP7 = 0x42 // Indirect mode, one write-twice register, to PPU
BBAD7 = .lobyte(BG1HOFS) // B-bus address
A1T7 = .loword(IndirectHdmaTable) // HDMA Table A-bus address
B1B7 = .bankbyte(IndirectHdmaTable)
DASB7 = .bankbyte(ContiguousArray) // Indirect HDMA bank
// Enable HDMA channel 7
// (HDMAEN should be written to during VBlank)
HDMAEN = 1 << 7
// Contiguous array of `BG1HOFS` values for all 244 scanlines.
// 224 words (448 bytes)
ContiguousArray:
dw 367, 366, 365, 364, 363, 362, 361, 360, 359, 358, 357, 356, 355, 354, 353, 352, 351, 350, 349, 348, 347, 346, 345, 344, 343, 342, 341, 340, 339, 338, 337, 336, 335, 334, 333, 332, 331, 330, 329, 328, 327, 326, 325, 324, 323, 322, 321, 320, 319, 318, 317, 316, 315, 314, 313, 312, 311, 310, 309, 308, 307, 306, 305, 304, 303, 302, 301, 300, 299, 298, 297, 296, 295, 294, 293, 292, 291, 290, 289, 288, 287, 286, 285, 284, 283, 282, 281, 280, 279, 278, 277, 276, 275, 274, 273, 272, 271, 270, 269, 268, 267, 266, 265, 264, 263, 262, 261, 260, 259, 258, 257, 256, 255, 254, 253, 252, 251, 250, 249, 248, 247, 246, 245, 244, 243, 242, 241, 240, 239, 238, 237, 236, 235, 234, 233, 232, 231, 230, 229, 228, 227, 226, 225, 224, 223, 222, 221, 220, 219, 218, 217, 216, 215, 214, 213, 212, 211, 210, 209, 208, 207, 206, 205, 204, 203, 202, 201, 200, 199, 198, 197, 196, 195, 194, 193, 192, 191, 190, 189, 188, 187, 186, 185, 184, 183, 182, 181, 180, 179, 178, 177, 176, 175, 174, 173, 172, 171, 170, 169, 168, 167, 166, 165, 164, 163, 162, 161, 160, 159, 158, 157, 156, 155, 154, 153, 152, 151, 150, 149, 148, 147, 146, 145, 144
// Indirect HDMA Table for the `BG1HOFS` register (one register, write twice transfer pattern).
IndirectHdmaTable:
// Cannot fit all 224 scanlines in a single HDMA entry.
// Splitting the table into two equally sized entries.
db 0x80 | 112 // 112 scanlines, repeat entry
// Word address pointing to the first half of ContiguousArray
dw ContiguousArray
db 0x80 | 112 // 112 scanlines, repeat entry (+112 = 224 scanlines total)
// Word address pointing to the second half of ContiguousArray
dw ContiguousArray + 112 * 2
db 0 // End HDMA table
Indirect mode can also be used to map the same contiguous array multiple times, creating a repeating HDMA effect.
DMAP7 = 0x42 // Indirect mode, one write-twice register, to PPU
BBAD7 = .lobyte(BG1HOFS) // B-bus address
A1T7 = .loword(IndirectHdmaTable) // HDMA Table A-bus address
B1B7 = .bankbyte(IndirectHdmaTable)
DASB7 = .bankbyte(SineTable) // Indirect HDMA bank
// Enable HDMA channel 7
// (HDMAEN should be written to during VBlank)
HDMAEN = 1 << 7
// Array of `BG1HOFS` values for every scanline
// 48 words (96 bytes)
SineTable:
// Sine wave, calculated using python:
// >>> import math
// >>> [ round(16.5 * math.sin(math.radians(i * 360 / 48))) for i in range(48) ]
dw 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 15, 14, 13, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2, 0, -2, -4, -6, -8, -10, -12, -13, -14, -15, -16, -16, -16, -16, -16, -15, -14, -13, -12, -10, -8, -6, -4, -2
// Indirect HDMA Table for the `BG1HOFS` register (one register, write twice transfer pattern).
IndirectHdmaTable:
db 0x80 | 48 // 48 scanlines, repeat
// Word address to BG1HOFS data
dw SineTable
db 0x80 | 48 // 48 scanlines, repeat
dw SineTable
db 0x80 | 48 // 48 scanlines, repeat
dw SineTable
db 0x80 | 48 // 48 scanlines, repeat
dw SineTable
db 0x80 | 48 // 48 scanlines, repeat
dw SineTable
db 0 // End HDMA table
// Not required. HDMA ends at the Vertical Blanking Period.
Dynamic HDMA tables
To prevent screen tearing or glitches, dynamic HDMA effects must not modify the HDMA registers or HDMA tables while they are in use. This can be achieved by either:
- Precalculating the HDMA tables (stored in ROM or decompressed/calculated into RAM) and changing the HDMA table address (A1Tn / A1Bn) to the next HDMA table during VBlank.
- Modifying the HDMA tables inside the VBlank routine.
- Double buffering the HDMA table.
Modifying HDMA tables during VBlank
Since the HDMA controller is deactivated during the Vertical Blanking Period, it is safe to write to a HDMA table in RAM inside the VBlank routine. If the changes to the table are minor, this can be easier and faster then a double-buffed HDMA table.
This technique is useful for adjusting the scanline height of HDMA entries over time.
When the screen is active, ensure the HDMA table and HDMA registers are only modified during VBlank to prevent screen tearing and glitches.
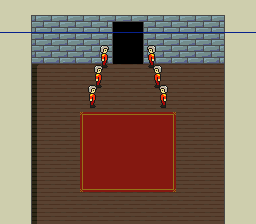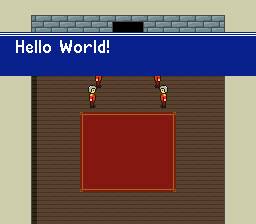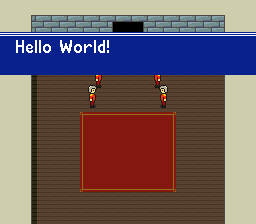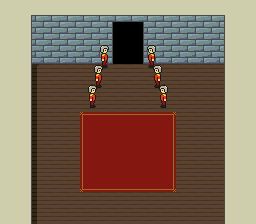
The following example takes the HDMA table from the textbox example above and modifies the Line-Counter byte of the second HDMA entry to create a textbox wipe animation. When textboxHeight is 0, only the first HDMA entry is processed and the textbox will not be visible. When textboxHeight is between 1-128, the second and third HDMA entries will be processed, and the textbox will be onscreen for textboxHeight scanlines.
Variables:
hdmaBuffer u8[64] - Buffer to store HDMA table
textboxHeight u8 - Visible textbox height, in scanlines. MUST BE <= 128.
state enum - The current state of the textbox wipe animation
// TIMING: Force-Blank, HDMA disabled
subroutine SetupHdma_TextboxWipeAnimation:
memcopy(HdmaTable, hdmaBuffer)
textboxHeight = 0
// Setup Hdma registers
DMAP7 = 0 // one register, to PPU
BBAD7 = .lobyte(TM) // B-bus address
A1T7 = .loword(hdmaBuffer) // HDMA Table A-bus address
B1B7 = .bankbyte(hdmaBuffer)
// TIMING: Screen active, in VBlank
subroutine VBlank_TextboxWipeAnimation:
// Modify HDMA table.
// Set the height of the second HDMA entry
hdmaBuffer[2] = textboxHeight
// Enable HDMA channel 7
HDMAEN = 1 << 7
// Called once per frame in the MainLoop
subroutine Process_TextboxWipeAnimation:
if state == OPEN_TEXTBOX:
textboxHeight = min(textboxHeight + 1, 64)
else if state == CLOSE_TEXTBOX:
textboxHeight = max(textboxHeight - 1, 0)
// HDMA Table for the `TM` register (one register transfer pattern).
HdmaTable:
db 32 // 32 scanlines, non-repeat entry
db 0x13 // TM = BG1, BG2, OBJ
db 64 // 64 scanlines, non-repeat entry (This is the byte that is modified by VBlank_TextboxWipeAnimation)
db 0x04 // TM = BG3
db 1 // 1 scanline, non-repeat entry
db 0x13 // TM = BG1, BG2, OBJ
db 0 // End HDMA table
Double buffered HDMA tables
Variables:
hdmaBufferA u8[512] - first HDMA buffer
hdmaBufferB u8[512] - second HDMA buffer
activeHdmaBuffer u8 - Flag to determine which buffer to write to
cameraX u16 - Camera's X position
// TIMING: Force-Blank, HDMA disabled
// Uses HDMA channel 7
subroutine Setup:
assert .bankbyte(hdmaBufferA) == .bankbyte(hdmaBufferB)
DMAP7 = 2 // one write-twice register, to PPU
BBAD7 = .lobyte(BG1HOFS) // B-bus address
B1B7 = .bankbyte(hdmaBufferA) // HDMA Table A-bus bank
// HDMA Table address is written during VBlank
// The hdmaBuffer must be populated before the next VBlank routine
BuildHdmaTable()
// TIMING: Screen active, in VBlank
// TIMING: MUST NOT be executed in a lag frame
// Uses HDMA channel 7
subroutine VBlank:
// Set HDMA table word address (depending on which buffer was last used by the MainLoop)
if activeHdmaBuffer == 0:
A1T7 = .loword(hdmaBufferB)
else:
A1T7 = .loword(hdmaBufferA)
// Enable HDMA channel 7
HDMAEN = 1 << 7
// TIMING: MUST NOT be called more than once per frame
function GetNextHdmaBuffer() -> *u8
if activeHdmaBuffer == 0:
activeHdmaBuffer = 1
return &hdmaBufferA
else:
activeHdmaBuffer = 0
return &hdmaBufferB
// TIMING: MUST NOT be called more than once per frame
subroutine BuildHdmaTable:
buffer = GetNextHdmaBuffer()
// Four non-repeat HDMA entries
// Remember, all `u8` writes MUST be <= 128
buffer[ 0] as u8 = 45
buffer[ 1] as u16 = cameraX >> 3
buffer[ 3] as u8 = 22
buffer[ 4] as u16 = cameraX >> 2
buffer[ 6] as u8 = 128
buffer[ 7] as u16 = cameraX
buffer[ 9] as u8 = 128
buffer[10] as u16 = cameraX << 1
// End HDMA table
buffer[12] as u8 = 0
Links
- HDMA Examples - by nesdoug
- Grog's Guide to DMA and HDMA on the SNES - superfamicom.org wiki