HDMA examples: Difference between revisions
(→HDMA Tables: Add Repeating HDMA entries) |
(→HDMA Tables: Replaced Line-Counter bitmasks with ranges.) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
== HDMA Tables == | == HDMA Tables == | ||
HDMA tables are made up of multiple HDMA entries. Each entry starts with a [[DMA_registers#NLTRn|Line-Counter]] byte, followed by register data. | HDMA tables are made up of multiple HDMA entries. Each entry starts with a [[DMA_registers#NLTRn|Line-Counter]] byte, followed by register data. The type of HDMA entry depends on the ''Line-Counter'' byte: | ||
* ''Line-Counter'' 0: End of HDMA table. The HDMA channel will be deactivated and will remain deactivated until the start of the next frame (even if <tt>HDMAEN</tt> is written to mid-frame). | |||
* ''Line-Counter'' 0x01-0x80: non-repeating HDMA entry. Writes once then waits <tt>''LineCounter''</tt> scanlines. | |||
* ''Line-Counter'' 0x81-0xFF: repeating HDMA entry. Writes every scanline for the next <tt>''LineCounter'' - 0x80</tt> scanlines. | |||
=== Non-repeat HDMA entries === | === Non-repeat HDMA entries === | ||
A non-repeat HDMA entry ( | A non-repeat HDMA entry (<tt>0x01 <= ''Line-Counter'' <= 0x80</tt>) is <tt>hdma_transfer_bytes + 1</tt> bytes in size. It consists of the ''Line-Counter'' byte, followed by the data to transfer on the next Horizontal Blanking Period. Afterwards, the HDMA controller will wait for ''Line-Counter'' scanlines before processing the next HDMA entry. | ||
| Line 149: | Line 139: | ||
=== Repeating HDMA entries === | === Repeating HDMA entries === | ||
A repeating HDMA entry (''Line-Counter'' | A repeating HDMA entry (''Line-Counter'' >= <tt>0x81</tt>) is <tt>hdma_transfer_bytes * (line_counter - 0x80) + 1</tt> bytes in size. It consists of the ''Line-Counter'' byte, followed by ''count'' (<tt>line_counter - 0x80</tt>) values to transfer. For the next ''count'' scanlines, the HDMA controller will transfer <tt>hdma_transfer_bytes</tt> bytes of data during the next ''count'' Horizontal Blanking Periods. | ||
Each repeating HDMA entry is a maximum of 127 scanlines tall. Any repeating HDMA entry with more than 127 scanlines must be split in two. | Each repeating HDMA entry is a maximum of 127 scanlines tall. Any repeating HDMA entry with more than 127 scanlines must be split in two. | ||
Revision as of 02:08, 26 November 2022
Examples for using HDMA.
Transfer patterns
The following is a suggested list of PPU registers that can be used in the various HDMA transfer patterns.
One register (DMAP pattern 0)
This pattern reads/writes a single byte to a single address on the B-bus (+0).
This pattern should not be used on write-twice or read-twice registers.
- BG Mode:
BGMODE - Mosaic Settings:
MOSAIC - BG Settings:
BG1SC,BG2SC,BG3SC,BG4SC,BG12NBA,BG34NBA - Mode 7 settings:
M7SEL - CGRAM address:
CGADD- A future HDMA channel should write to
CGDATAon the same scanline as theCGADDwrite.
- A future HDMA channel should write to
- Window settings:
W12SEL,W34SEL,WOBJSEL,WBGLOG,WOBJLOG - Layer enable:
TM,TS,TMW,TSW - Color math:
CGWSEL,CGADSUB - Screen Mode/Video Select:
SETINI - Fixed color data:
COLDATA- Only a single B/G/R channel can be changed in this pattern (unless multiple channels contain the same value). See
COLDATAfor more details.
- Only a single B/G/R channel can be changed in this pattern (unless multiple channels contain the same value). See
Two registers (DMAP pattern 1)
This pattern reads/writes two bytes to two addresses on the B-bus (+0, +1). It is useful when writing to two adjacent byte registers.
This pattern must not be used on write-twice or read-twice registers.
- Window 1 left and right position:
WH0&WH1 - Window 2 left and right position:
WH2&WH3 - Window mask settings:
W12SEL&W34SEL,W34SEL&WOBJSEL - Window mask logic:
WBGLOG&WOBJLOG - Layer Enable:
TM&TS,TMW&TSW - Color math settings:
CGWSEL&CGADSUB
One register, write twice (DMAP pattern 2)
This pattern reads/writes two bytes to a single write-twice or read-twice register on the B-bus (+0, +0).
- BG horizontal scroll offset:
BGnHOFS - BG vertical scroll offset:
BGnVOFS - Mode 7 matrix:
M7A,M7B,M7C,M7D,M7X,M7Y - CGRAM data:
CGDATA- Note: A previous HDMA channel should set the CGRAM address on the same scanline as a
CGDATAwrite
- Note: A previous HDMA channel should set the CGRAM address on the same scanline as a
- Fixed color data:
COLDATA- Only two of the three B/G/R channels can be changed in this pattern (unless two channels share the same value). See
COLDATAfor more details.
- Only two of the three B/G/R channels can be changed in this pattern (unless two channels share the same value). See
Two registers, write twice (DMAP pattern 3)
This pattern reads/writes four bytes to two adjacent write-twice or read-twice registers on the B-bus (+0, +0, +1, +1).
- BG scroll offsets:
BGnHOFS&BGnVOFS - 2 adjacent mode 7 matrix values:
M7A&M7B,M7C&M7D,M7X&M7Y - CGRAM address and data:
CGADD&CGDATA- This transfer will write two values to the CGRAM address, followed by a color word value to
CGDATA. - The first byte will be ignored by the PPU, the second byte contains the target CGRAM address (palette index), the third and forth bytes contain the color data.
- This transfer will write two values to the CGRAM address, followed by a color word value to
Four registers (DMAP pattern 4)
This pattern reads/writes four bytes to four addresses on the B-bus (+0, +1, +2, +3).
This pattern must not be used on write-twice or read-twice registers.
- All four window positions:
WH0&WH1&WH2&WH3
HDMA Tables
HDMA tables are made up of multiple HDMA entries. Each entry starts with a Line-Counter byte, followed by register data. The type of HDMA entry depends on the Line-Counter byte:
- Line-Counter 0: End of HDMA table. The HDMA channel will be deactivated and will remain deactivated until the start of the next frame (even if HDMAEN is written to mid-frame).
- Line-Counter 0x01-0x80: non-repeating HDMA entry. Writes once then waits LineCounter scanlines.
- Line-Counter 0x81-0xFF: repeating HDMA entry. Writes every scanline for the next LineCounter - 0x80 scanlines.
Non-repeat HDMA entries
A non-repeat HDMA entry (0x01 <= Line-Counter <= 0x80) is hdma_transfer_bytes + 1 bytes in size. It consists of the Line-Counter byte, followed by the data to transfer on the next Horizontal Blanking Period. Afterwards, the HDMA controller will wait for Line-Counter scanlines before processing the next HDMA entry.
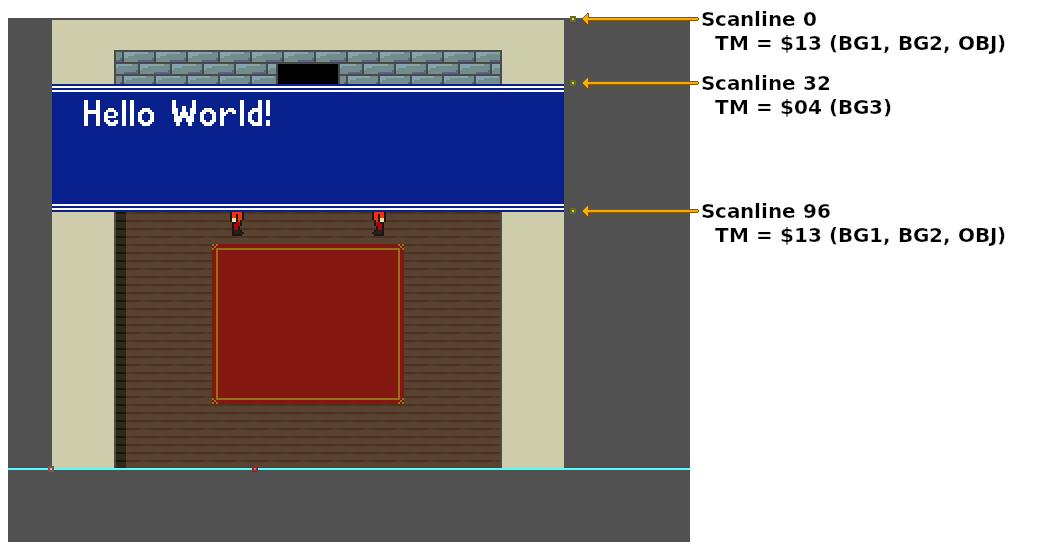
// HDMA Table targeting the `TM` register (One register transfer pattern).
HdmaTable:
db 32 // 32 scanlines, non-repeat entry
db 0x13 // TM = BG1, BG2, OBJ
db 64 // 64 scanlines, non-repeat entry
db 0x04 // TM = BG3
db 1 // 1 scanline, non-repeat entry
db 0x13 // TM = BG1, BG2, OBJ
db 0 // End HDMA table
Each non-repeat HDMA entry is a maximum of 128 scanlines tall. Any HDMA entry with more then 128 scanlines must be split in two, with each entry containing the same data values.
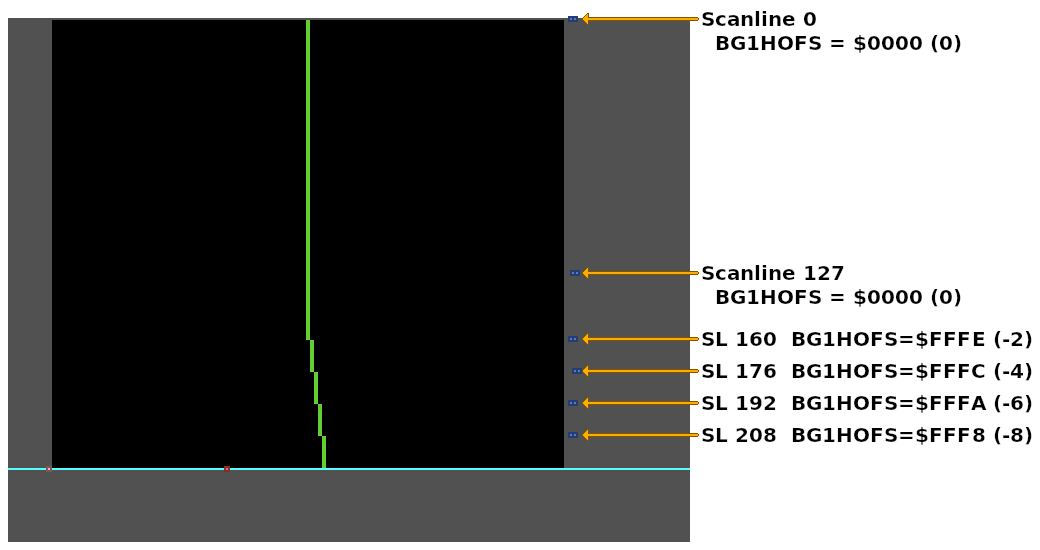
// HDMA Table for the `BG1HOFS` register (one register, write twice transfer pattern).
HdmaTable:
// 160 scanlines with BG1HOFS = 0
// Too many scanlines to fit in a single HDMA entry.
db 127 // 127 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw 0
db 33 // 33 scanlines, non-repeat entry (+127 = 160 scanlines total)
dw 0 // Same data value as the previous entry
// Change BG1HOFS every 16 scanlines
db 16 // 16 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw -2
db 16 // 16 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw -4
db 16 // 16 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw -6
db 16 // 16 scanlines, non-repeat entry
dw -8
db 0 // End HDMA table
Repeating HDMA entries
A repeating HDMA entry (Line-Counter >= 0x81) is hdma_transfer_bytes * (line_counter - 0x80) + 1 bytes in size. It consists of the Line-Counter byte, followed by count (line_counter - 0x80) values to transfer. For the next count scanlines, the HDMA controller will transfer hdma_transfer_bytes bytes of data during the next count Horizontal Blanking Periods.
Each repeating HDMA entry is a maximum of 127 scanlines tall. Any repeating HDMA entry with more than 127 scanlines must be split in two.
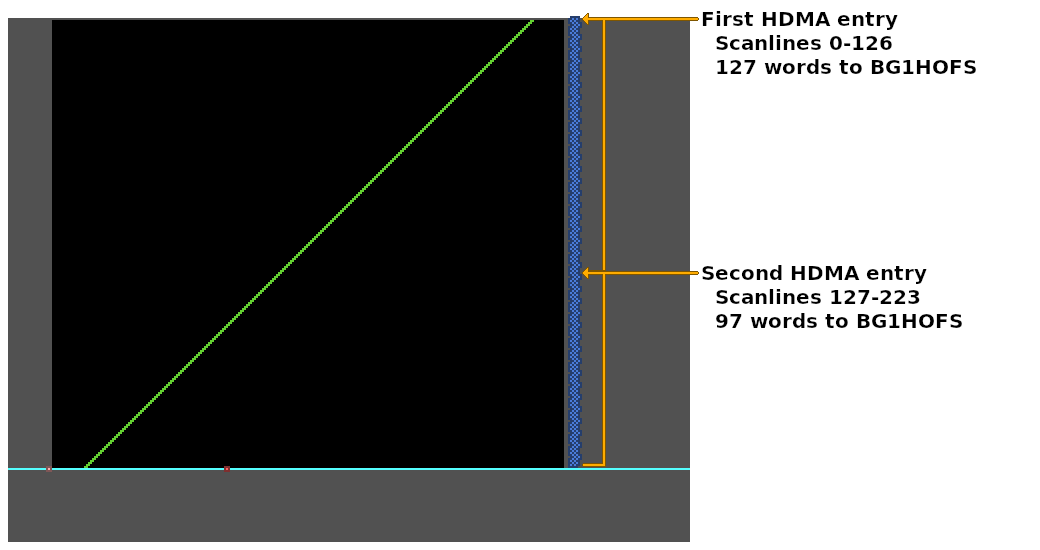
// HDMA Table for the `BG1HOFS` register (one register, write twice transfer pattern).
HdmaTable:
db 0x80 | 127 // 127 scanlines, repeat entry (maximum number of repeat scanlines per entry)
// 127 words (254 bytes) of BG1HOFS data for the next 127 scanlines
dw 144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149, 150, 151, 152, 153, 154, 155, 156, 157, 158, 159, 160, 161, 162, 163, 164, 165, 166, 167, 168, 169, 170, 171, 172, 173, 174, 175, 176, 177, 178, 179, 180, 181, 182, 183, 184, 185, 186, 187, 188, 189, 190, 191, 192, 193, 194, 195, 196, 197, 198, 199, 200, 201, 202, 203, 204, 205, 206, 207, 208, 209, 210, 211, 212, 213, 214, 215, 216, 217, 218, 219, 220, 221, 222, 223, 224, 225, 226, 227, 228, 229, 230, 231, 232, 233, 234, 235, 236, 237, 238, 239, 240, 241, 242, 243, 244, 245, 246, 247, 248, 249, 250, 251, 252, 253, 254, 255, 256, 257, 258, 259, 260, 261, 262, 263, 264, 265, 266, 267, 268, 269, 270
db 0x80 | 97 // 97 scanlines, repeat entry (+127 = 224 scanlines total)
// 97 words (194 bytes) of BG1HOFS data for the next 97 scanlines
dw 271, 272, 273, 274, 275, 276, 277, 278, 279, 280, 281, 282, 283, 284, 285, 286, 287, 288, 289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 296, 297, 298, 299, 300, 301, 302, 303, 304, 305, 306, 307, 308, 309, 310, 311, 312, 313, 314, 315, 316, 317, 318, 319, 320, 321, 322, 323, 324, 325, 326, 327, 328, 329, 330, 331, 332, 333, 334, 335, 336, 337, 338, 339, 340, 341, 342, 343, 344, 345, 346, 347, 348, 349, 350, 351, 352, 353, 354, 355, 356, 357, 358, 359, 360, 361, 362, 363, 364, 365, 366, 367
db 0 // End HDMA table
Links
- HDMA Examples - by nesdoug
- Grog's Guide to DMA and HDMA on the SNES - superfamicom.org wiki